DORA Regulation
DORA is a regulation established by the European supervisory authorities to enhance financial entities’ digital operational resilience. Its primary goal is to ensure these entities can effectively manage and mitigate risks associated with Information and Communication Technology (ICT) systems.
EU member states present DORA and set a comprehensive framework to safeguard financial institutions from ICT-related disruptions, including cyber-attacks, system failures, and data breaches.
Scope of DORA
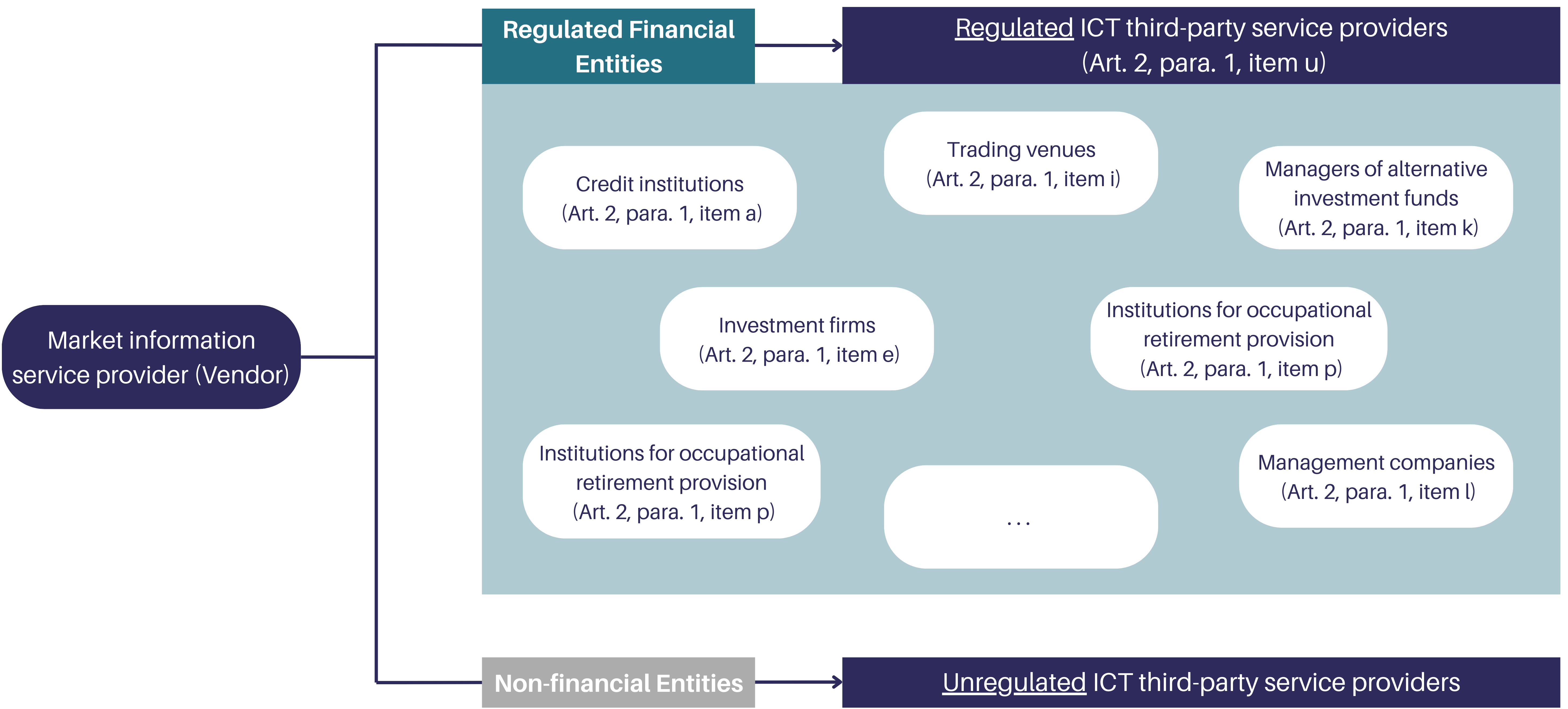
DORA requirements apply to various EU financial institutions and their critical ICT third-party service providers.
Five key DORA pillars
- 1. Risk Management framework
Managing ICT risks under DORA poses significant challenges for financial institutions. These tasks require significant effort and resources, from identifying and assessing a wide range of risks to integrating new frameworks with existing systems.
1.1 Implementing risk management frameworks
Implementing new ICT risk management frameworks that comply with DORA needs to be integrating them with existing systems.
1.2 Identifying and assessing ICT risks
Financial institutions must conduct thorough risk assessments to uncover all potential vulnerabilities within their ICT systems.
1.3 Impact of evolving threats and technological advances
The rapid evolution of cyber threats and technological advances add another layer of complexity to risk identification and assessment.
DORA Regulation (EU) 2022/2554, Articles 5-15 on ICT Risk Management, Final Report on draft RTS on ICT Risk Management Framework and on simplified ICT Risk Management Framework.
- 2. Third party risk management
DORA requires financial institutions to ensure that their ICT service providers meet stringent security and resilience standards given the reliance on external ICT service providers.
2.1 Thorough Due Diligence and Risk Assessment
Conducting thorough due diligence and risk assessments of third-party ICT providers is vital to ensure they meet required standards. Effective coordination and resource allocation are essential for managing multiple third-party provider relationships. Otherwise, one can face a situation when DORA noncompliance of a third-party provider affects everyone involved.
2.2 Ensure contracts include provisions for security and resilience
Contracts with third-party ICT service providers must include specific provisions to ensure security and resilience. These provisions should cover data protection, service level agreements (SLAs), and compliance with regulatory standards.
2.3 Continuously monitor third party performance and risks
Ongoing monitoring of third-party ICT service providers is essential to maintain compliance and manage risks effectively. This involves regular performance reviews, risk assessments, and updates to agreements as necessary.
DORA Regulation (EU) 2022/2554, Article 28 on ICT Third-Party Risk Management, Final Report on draft RTS to specify the policy on ICT services supporting critical or important functions.
- 3. Incident management and reporting
Incident management and reporting are critical components of DORA compliance. Financial institutions must have robust systems in place to detect, report and respond to ICT-related incidents in a timely and effective manner.
3.1 Incident classification and coordination across teams
These tasks require significant effort and coordination, from establishing systems for timely and accurate incident classification to coordinating across multiple teams. Financial institutions often receive a high volume of alerts, many of which may be false positives. Sifting through these alerts to identify real threats can be time consuming and resource intensive.
3.2 Establishing robust incident response plans
Robust incident response plans let banks respond quickly to incidents. The speed of response often depends on the quality of detection and precision of documentation.
3.3 Reporting significant incidents to relevant authorities
One of the key requirements of DORA is the timely and accurate reporting of ICT-related incidents.
DORA Regulation (EU) 2022/2554, Articles 15 and 16 on ICT Incident Management, Final Report on draft RTS on classification of major incidents and significant cyber threats.
- 4. Digital operational resilience testing
Digital operational resilience testing is essential for ensuring financial institutions can withstand and recover from ICT-related disruptions.
4.1 Conducting penetration tests
Regular resilience testing ensures that financial institutions can maintain strong defenses and respond quickly to threats.
4.2 Running disaster recovery drills
Disaster recovery drills ensure that systems can be restored quickly and effectively in case of a disaster. This includes testing backup systems to verify their functionality.
4.3 Balance between thorough testing and operational disruption
Digital operational resilience testing is essential for ensuring DORA compliance and maintaining robust defenses. While conducting regular and comprehensive tests, financial institutions must navigate challenges such as simulating realistic incidents and balancing thorough testing with operational continuity.
DORA Regulation (EU) 2022/2554, Articles 11 and 13 on Digital Operational Resilience Testing, Final Report on draft RTS on ICT Risk Management Framework and on simplified ICT Risk Management Framework.
- 5. Information sharing on cyber threats
Information sharing is a key component of DORA compliance. Financial institutions must work together to enhance collective security while balancing data privacy needs.
5.1 Establishing secure information-sharing channels
Establishing secure information-sharing channels enables financial institutions to stay ahead of emerging threats and enhance collective security.
5.2 Overcoming barriers to secure and efficient information sharing
Addressing data sensitivity and building trust is essential for effective and secure information sharing. Financial institutions can collaborate effectively while safeguarding data privacy by establishing secure information-sharing channels and implementing robust data protection measures.
DORA Regulation (EU) 2022/2554, Article 21 on Information Sharing, Final Report on draft RTS on classification of major incidents and significant cyber threats.
We can help those responsible for market data management to achieve DORA compliance!
Remember, being proactive about following the rules and preparing for potential issues to benefit from DORA is important. With years of experience in transforming market data administration into market data management for Europe’s leading financial firms, MDnomics‘ experts can guide you on your path to DORA compliance.